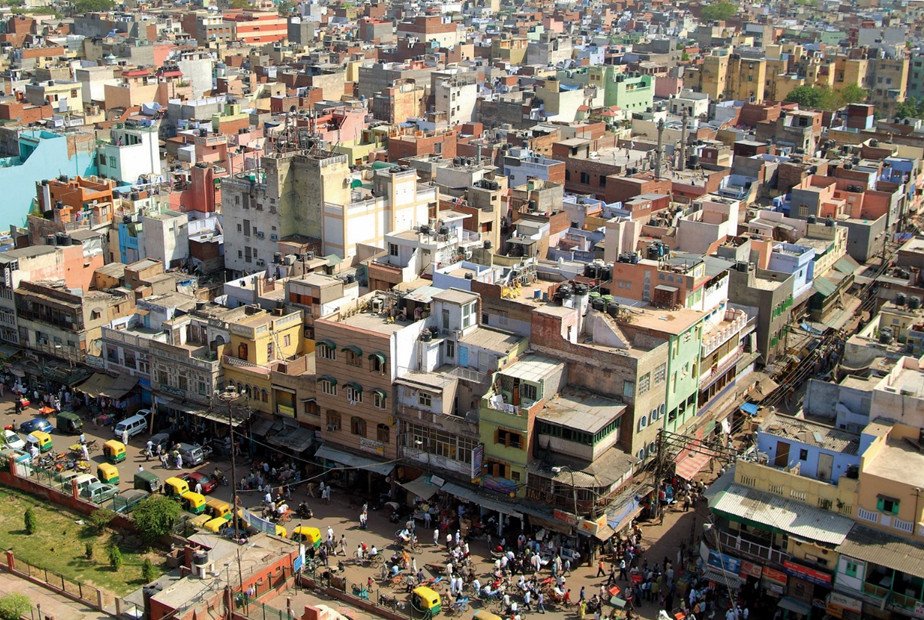
Learn more about EO4SD-URBAN
an ESA project aimed at deriving key geo-information products from Earth Observation
data in support of urban development programmes
Since 2008 the European Space Agency (ESA) has worked closely together with the International Financing Institutions (IFIs) and their Client States to harness the benefits of Earth Observation (EO) in their operations and resources management. In this context, Earth Observation for Sustainable Development (EO4SD) is a new ESA initiative, which aims at increasing the uptake of EO-based information in the IFIs regional and global programmes by means of a systematic user-driven approach.
Objectives
EO4SD-Urban aims at demonstrating the benefits of EO-based geo-information products and services to support urban planning tasks in the context of programs related to the IFIs and stakeholders in Client States. Specifically, its goals are:
To provide convincing demonstrations of the benefit and utility of EO-based information in the urban framework;
To provide the intended services on a regional basis for about 40 cities;
To ensure that the products and services are user-driven via a strong engagement with IFIs, stakeholders and Client States;
To provide an operational urban service portfolio offering quality controlled products;
To provide a technology transfer via capacity building exercises in the selected study regions;
To ensure a robust organization of service networks with the regional counterparts via dedicated local offices;
To develop new business opportunities in urban EO services for the European industry.
Portfolio
Based on the current state-of-the-art of satellite remote sensing and initial discussions with stakeholders, the current service portfolio outlines the preliminary composition of the information services/products which can be provided.
Have a look to the complete product portfolio brochure or browse some sample products by clicking the dedicated buttons below.
-
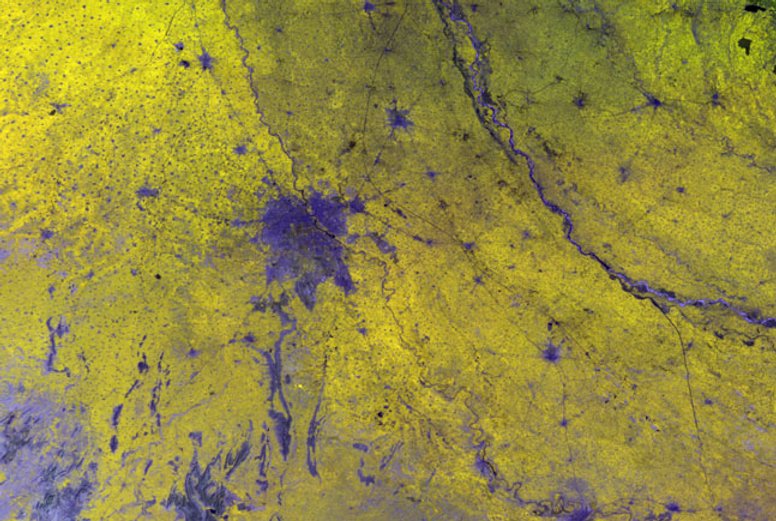
URBAN AND PERI-URBAN LAND USE / LAND COVER
Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) maps support a wide range of applications related to urban planning including spatial statistical analysis and are of great importance for understanding how development trends are affecting specific locations in urban areas. They are used operationally in a number of countries for identifying priorities for urban development and assessing the impact of previous investments based on change analyses.
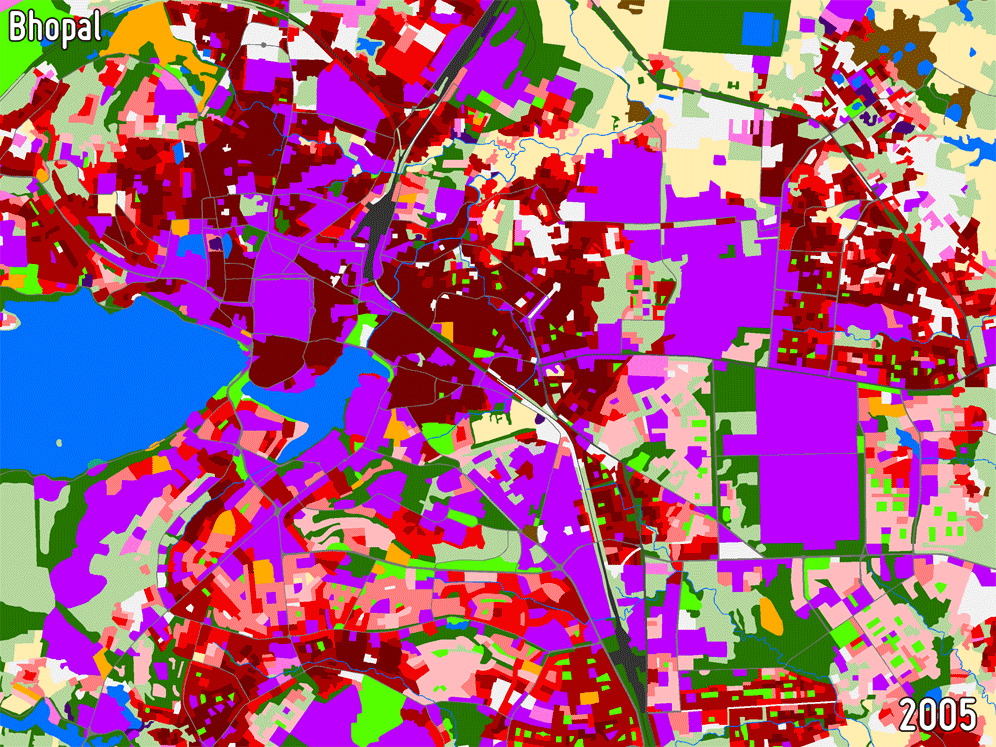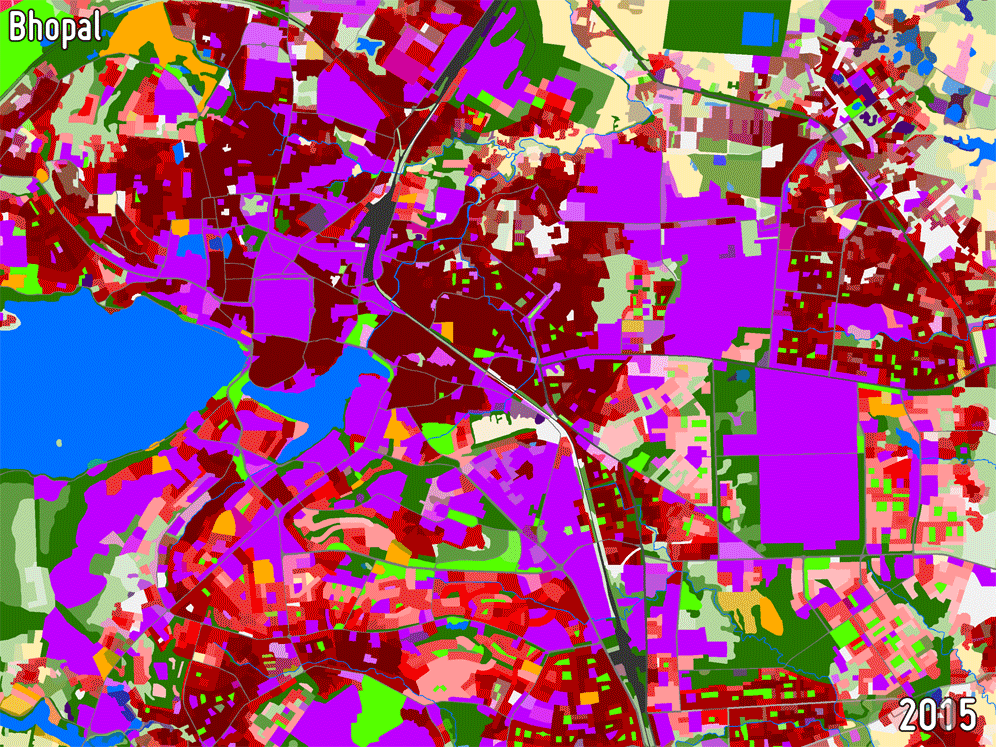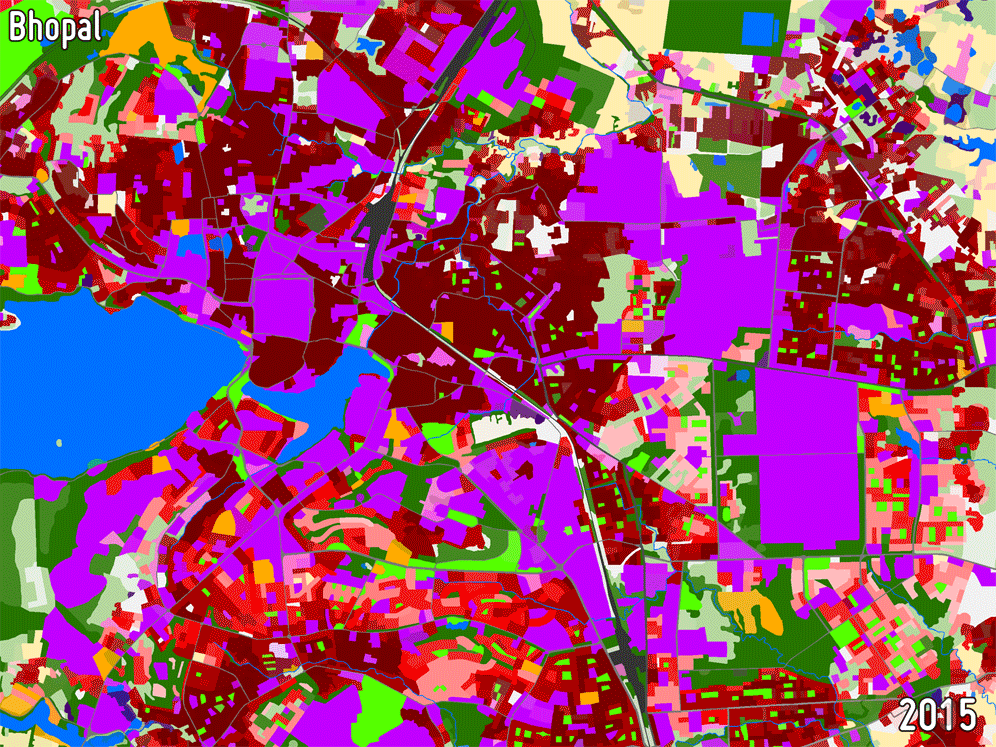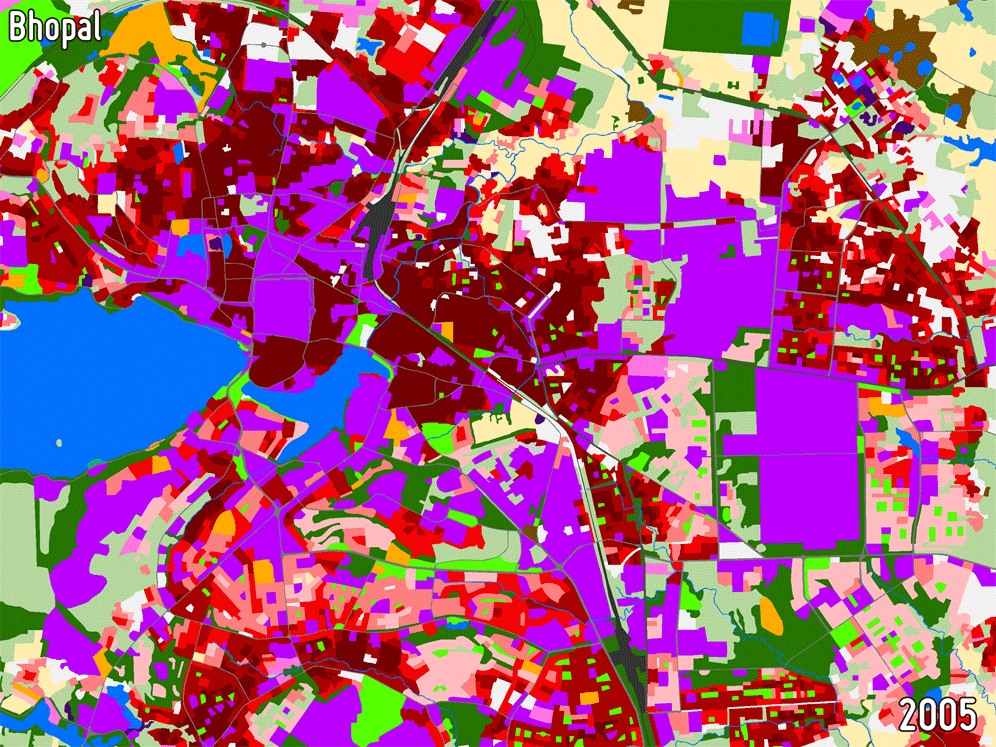
-
BUILDING FOOTPRINTS AND TYPES
Information about the spatial location of buildings in urban and peri-urban areas is a valuable baseline for several purposes. Topological analyses can be performed to distinguish different types of building blocks and generate different classes of housing density. Furthermore, with the integration of 3D information, volume and estimated space for living can modeled. In case of natural disasters the extent of damages can be also easily assessed.
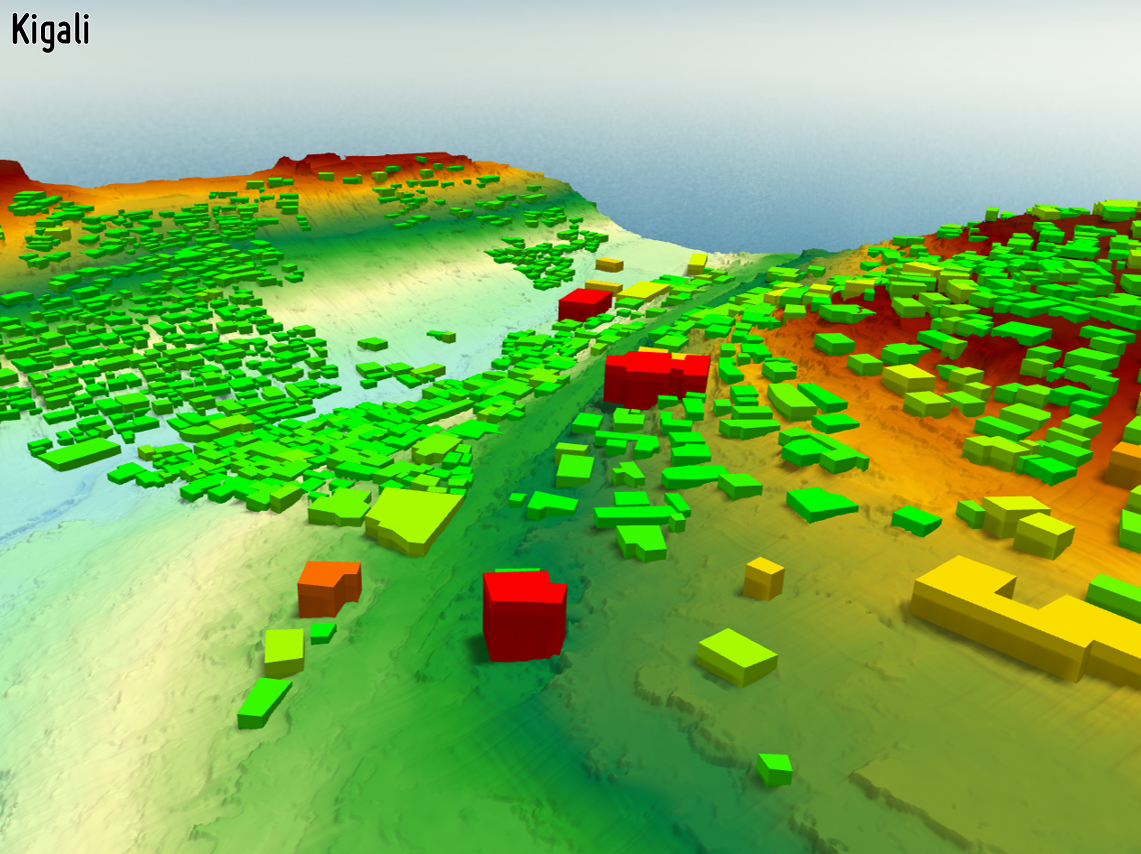
-
3D MODELS
3D models provide a proper delineation of the built-up area extent, as well as a precise estimation of building heights which are required for reliably characterizing the building volume; this also supports the estimation of population distribution. Building height is of great importance when modelling anthropogenic heat fluxes. Furthermore, height models in conjunction with building footprints can provide the Floor Area Ratio (FAR) required in many urban planning regulatory requirements.
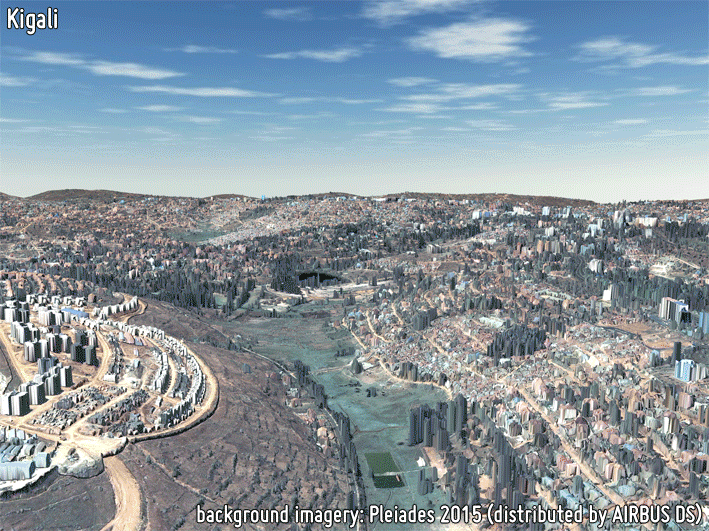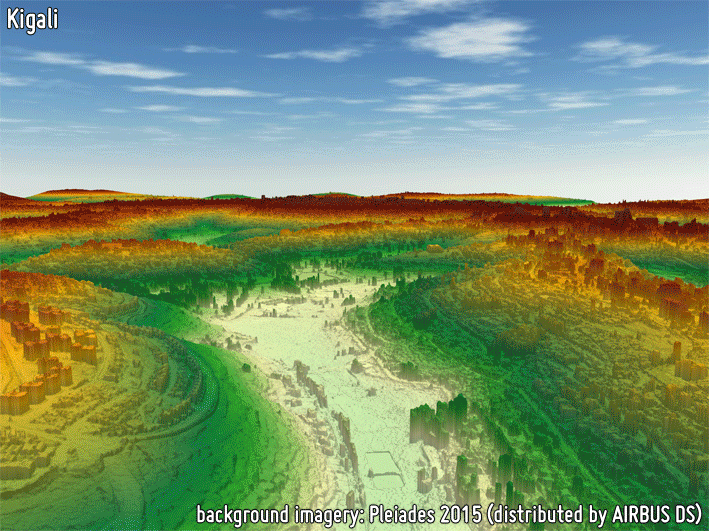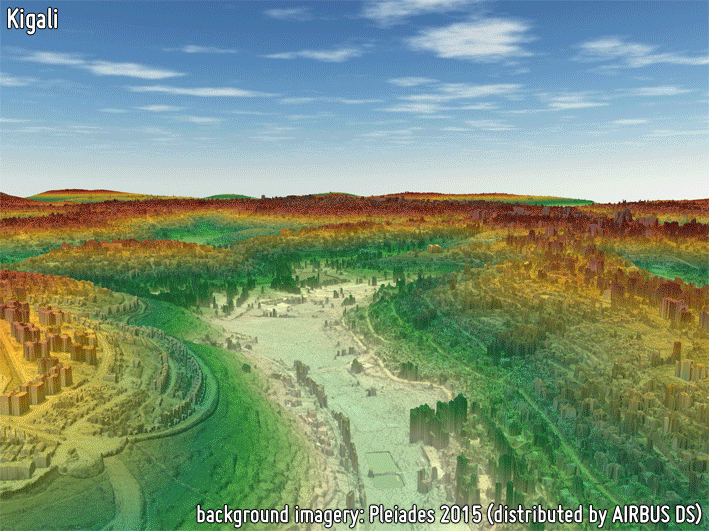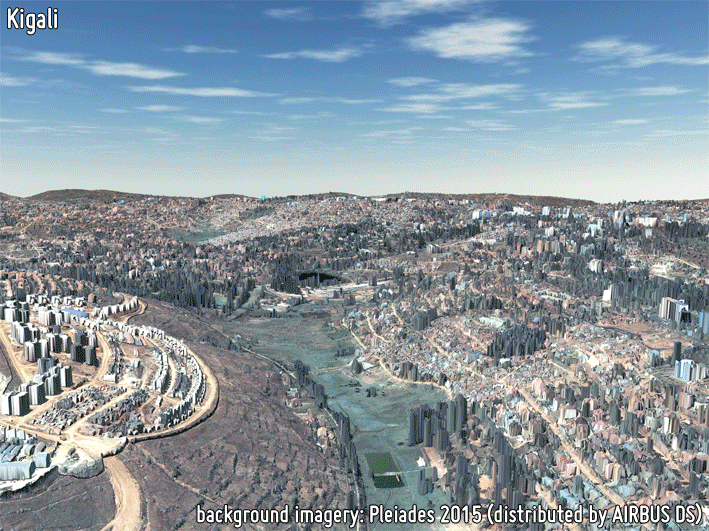
-
FLOOD HISTORY AND RISK ASSESSMENT
Mapping of historic flood events from both EO and non-EO data helps to assess the susceptibility of areas to future flooding. In combination with current land use information, a flood risk map can be produced. Based on such risk maps, adequate countermeasures can be taken at the city level.
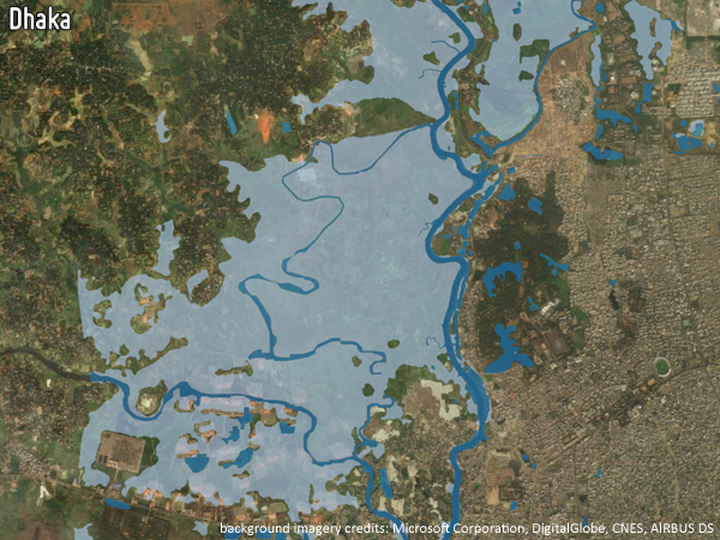
-
LAND SUBSIDENCE MAPPING
Land subsidence in cities not only poses a big problem for the stability of buildings and roads, but in coastal areas prone to global sea level rise it may become a prime cause of catastrophic flooding. Measurements from Sentinel-1 satellite allow for a precise monitoring of the subsidence rates and thus enable authorities to properly prepare for flooding events and initiate prevention measures.
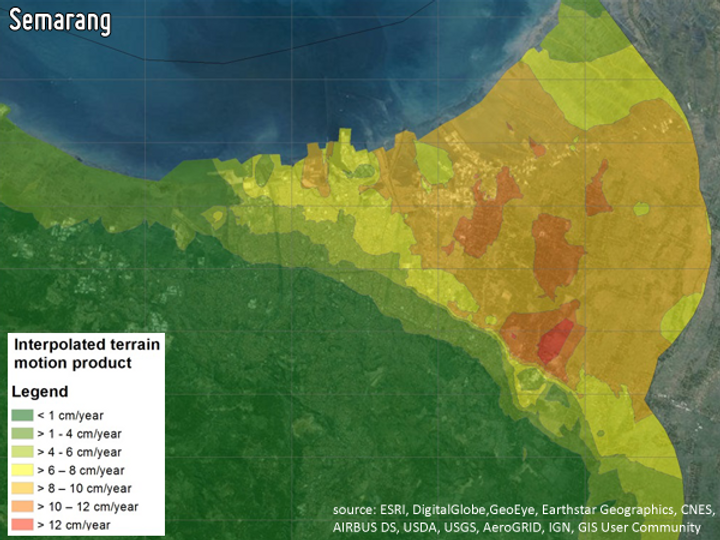
-
Reliably outlining settlement extent is fundamental for accurately estimating, among others, the population distribution, the use of resources, infrastructure and transport needs, socioeconomic development, human health and food security. Moreover, monitoring its temporal dynamics is of great support for properly modelling the ongoingurbanisation and, thus, better estimating future trends and implementing suitable planning strategies.
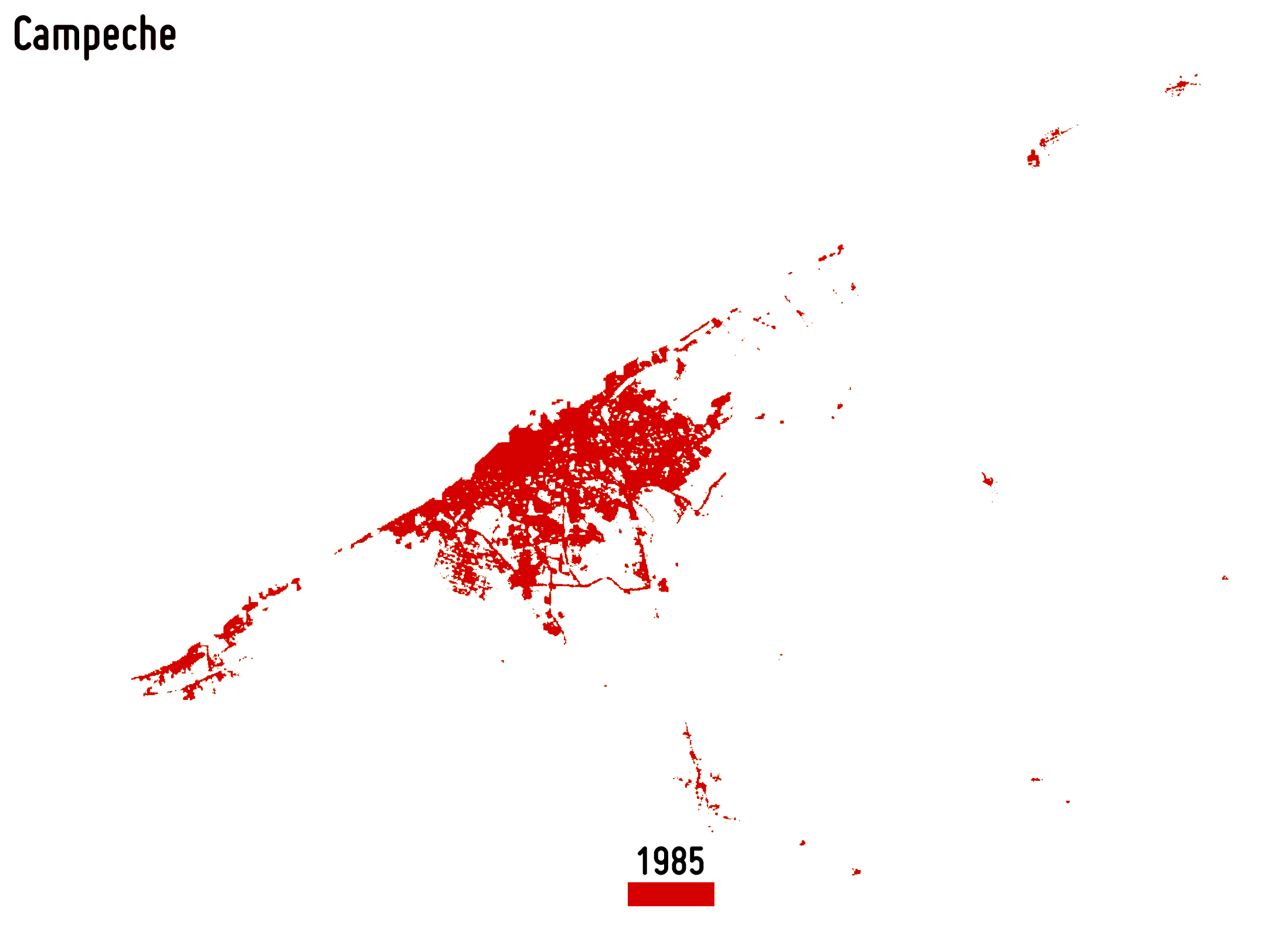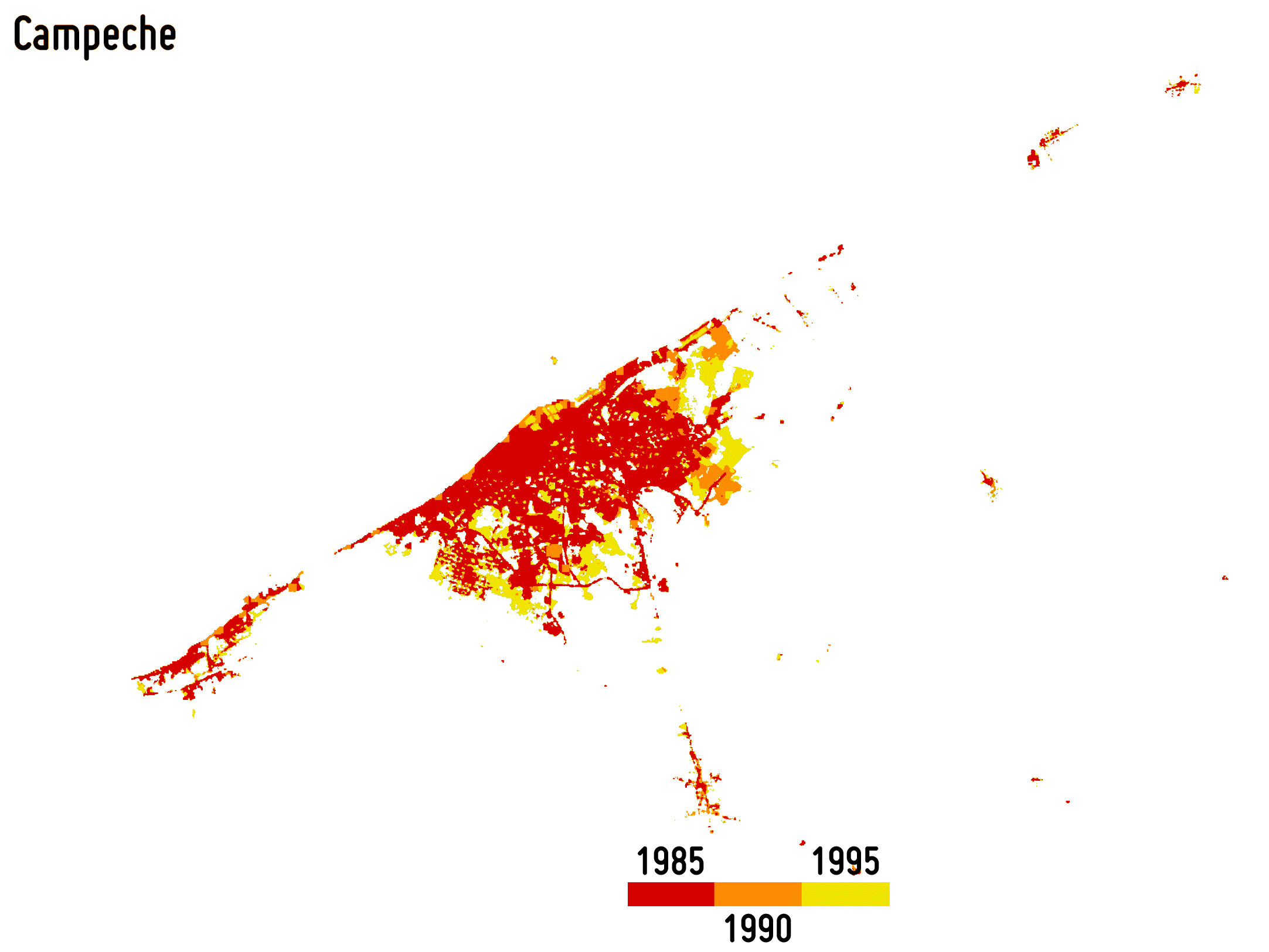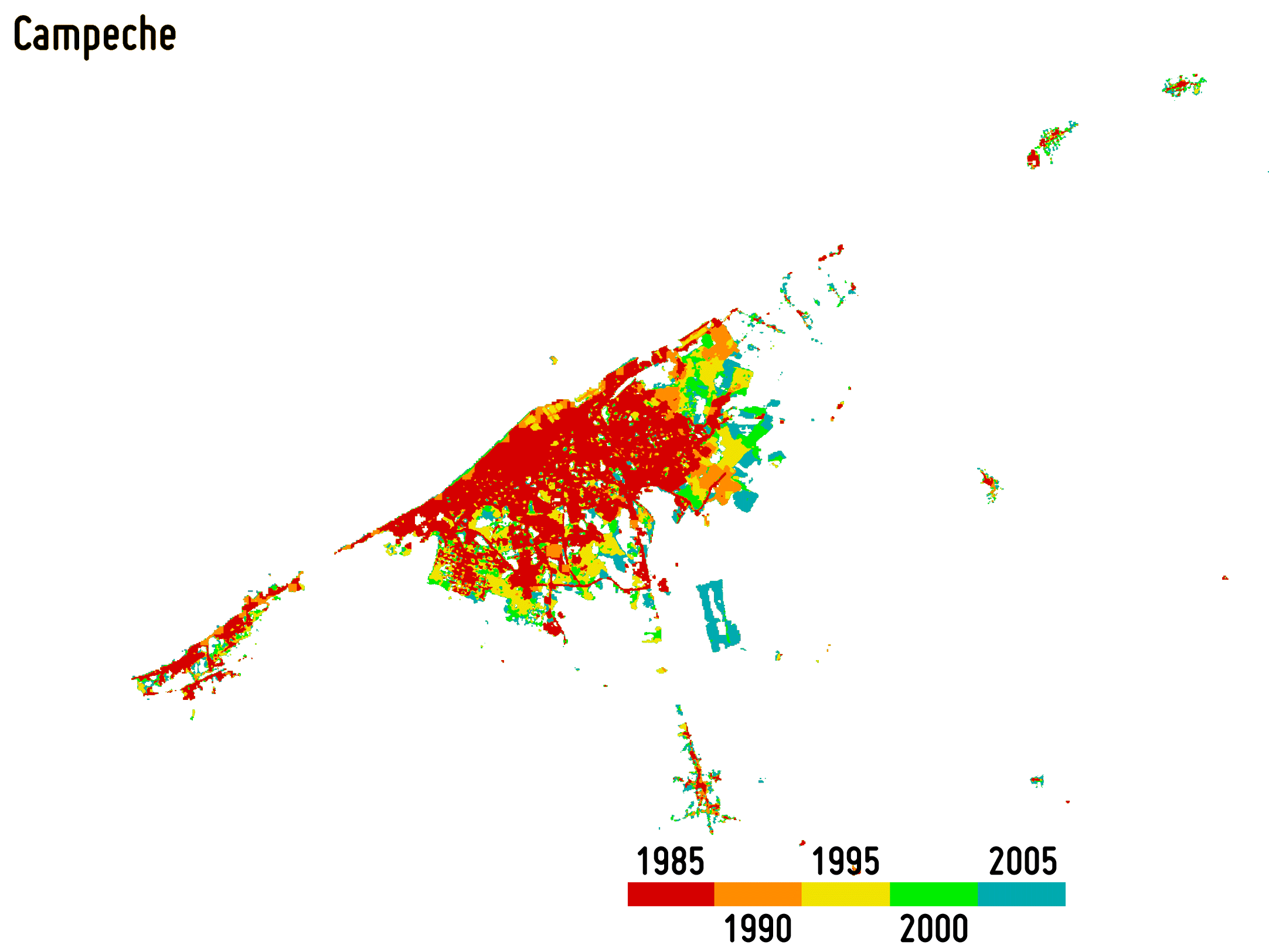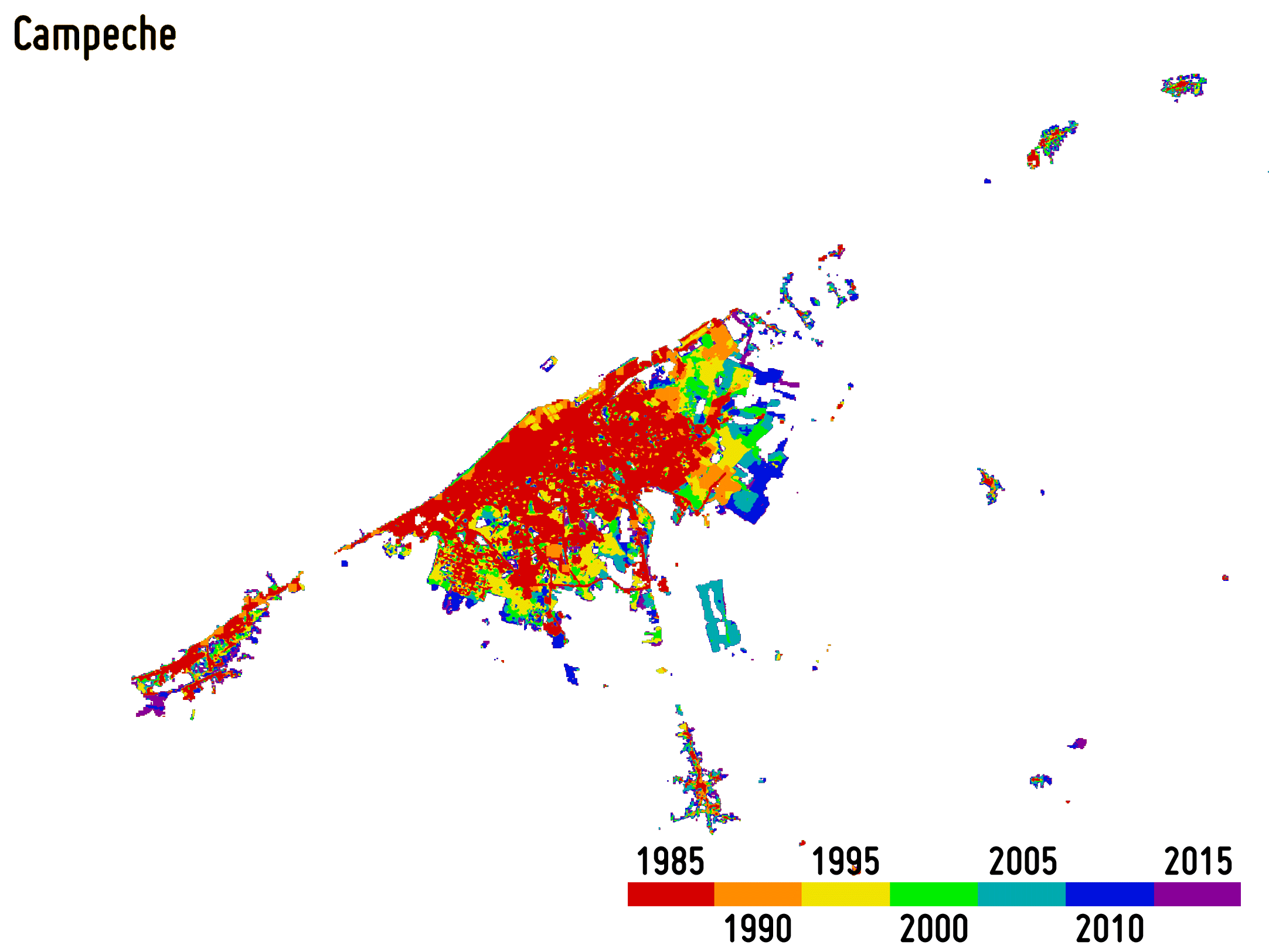
-
Settlement growth is associated not only to the construction of new buildings, but – more in general – to a consistent increase of all the impervious surfaces (e.g., parking lots, square, pavements, etc.), which do not allow water to penetrate, forcing it to run off. To effectively map the percentage impervious surface (PIS) and its change over time is then of key importance being it related to the risk of urban floods, the urban heat island phenomenon as well as the reduction of ecological productivity.
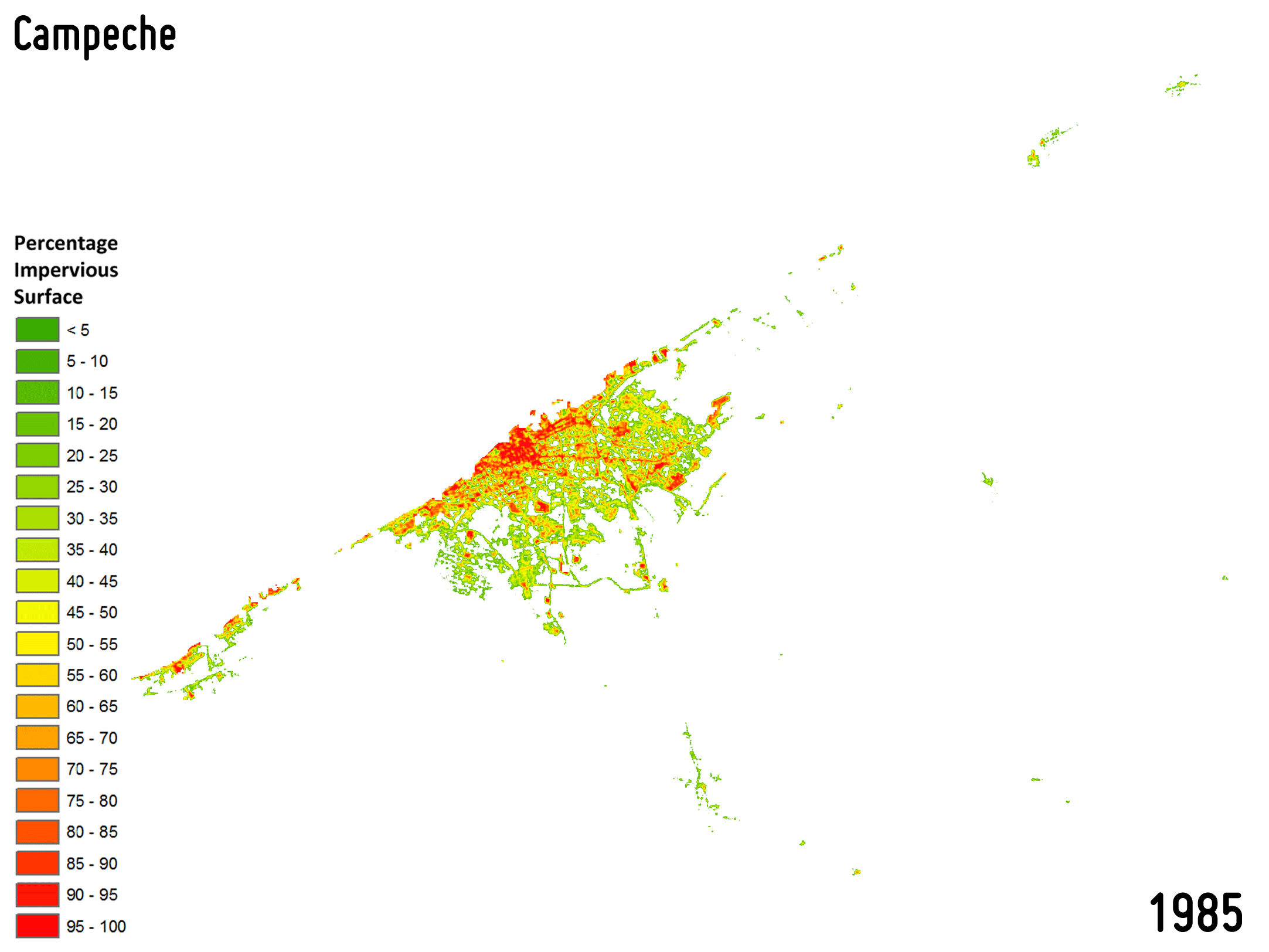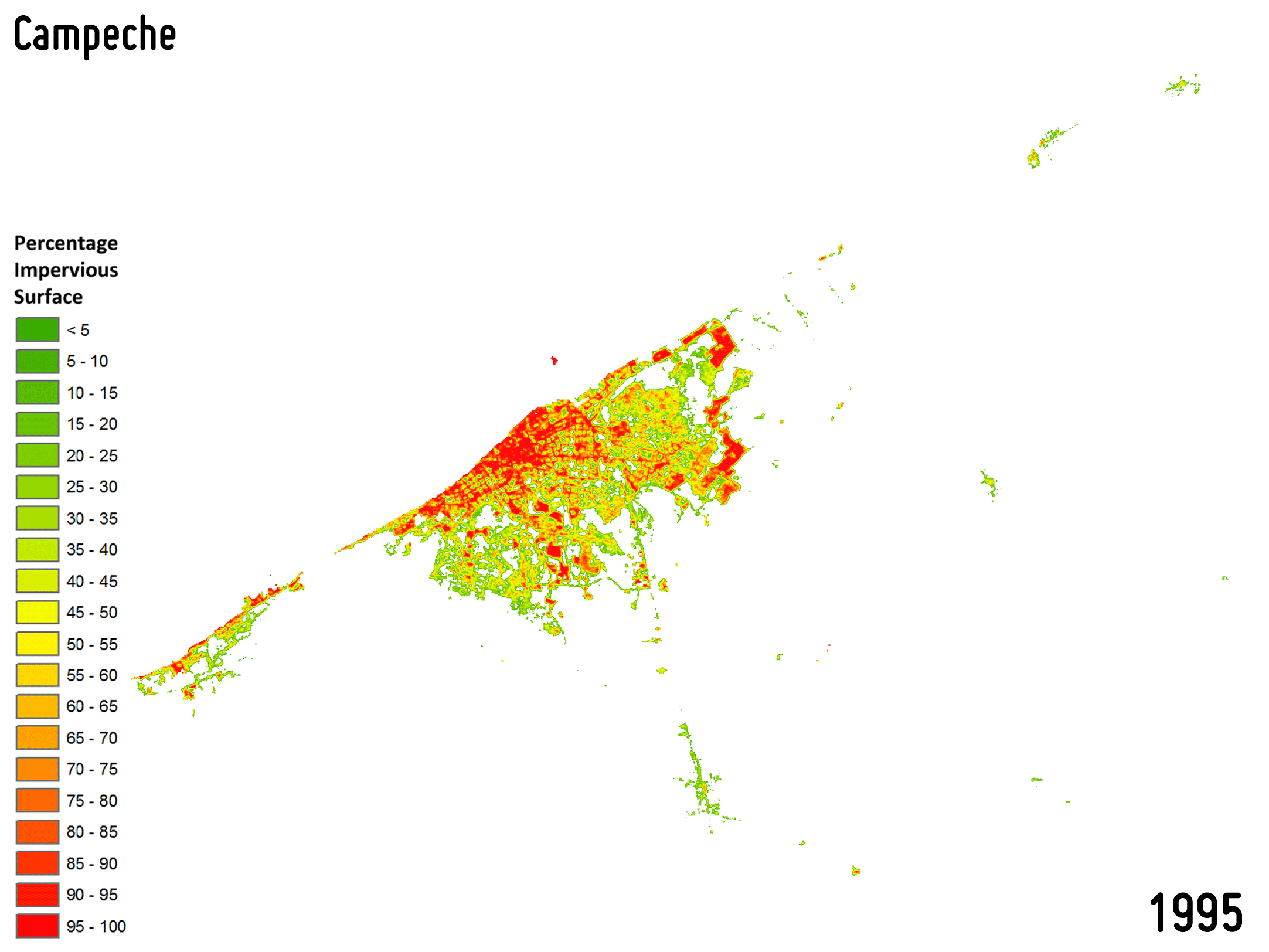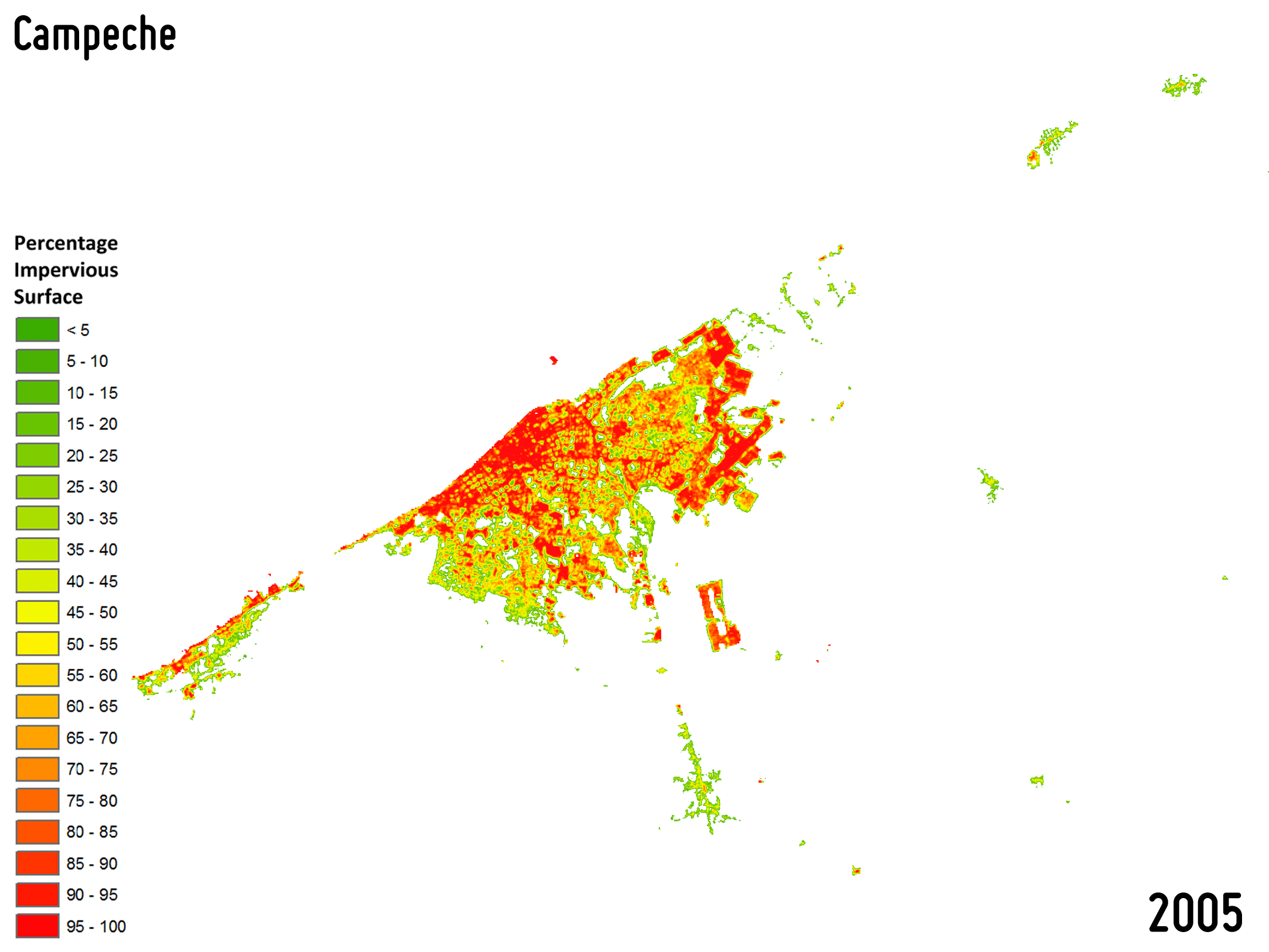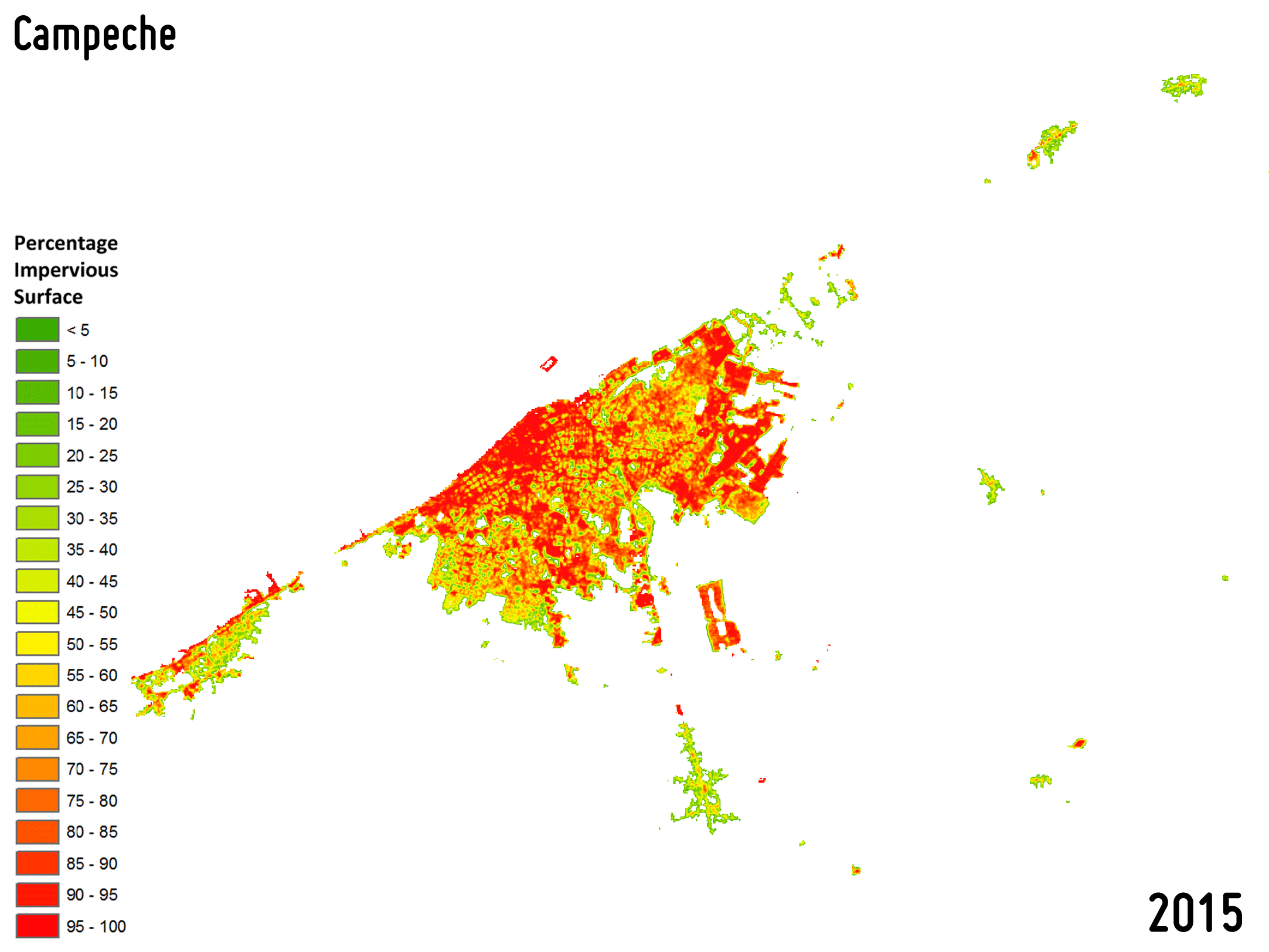
-
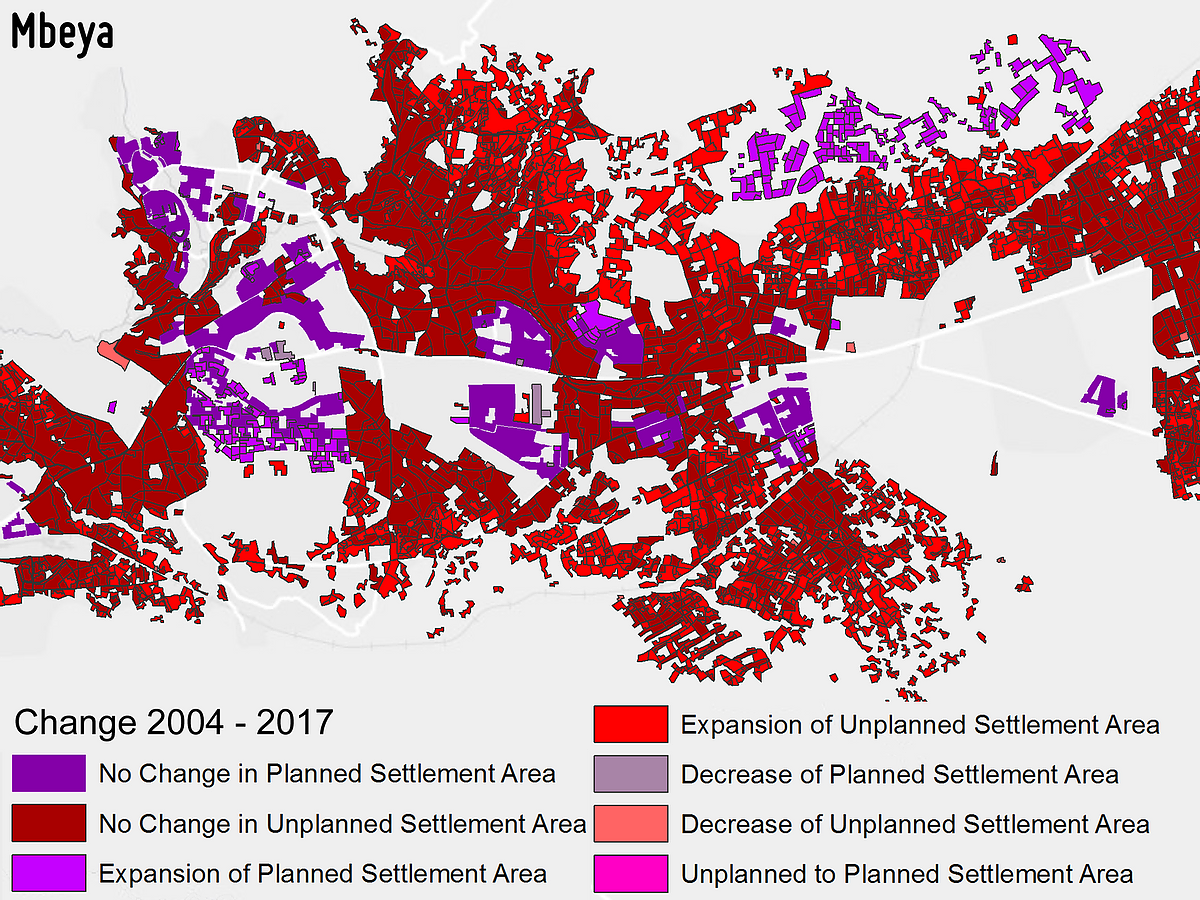
UNPLANNED SETTLEMENTS MONITORING
Monitoring unplanned settlements over time is fundamental for a sustainable urban planning. As they are dynamic with frequent population fluctuations, traditional field mapping is not effective due to high time and economic costs. Instead, very high spatial resolution EO imagery allows to cover wide areas at suitable temporal resolution, thus representing a unique planning tool for overall assessment and rehabilitation activities in and around their location.
-
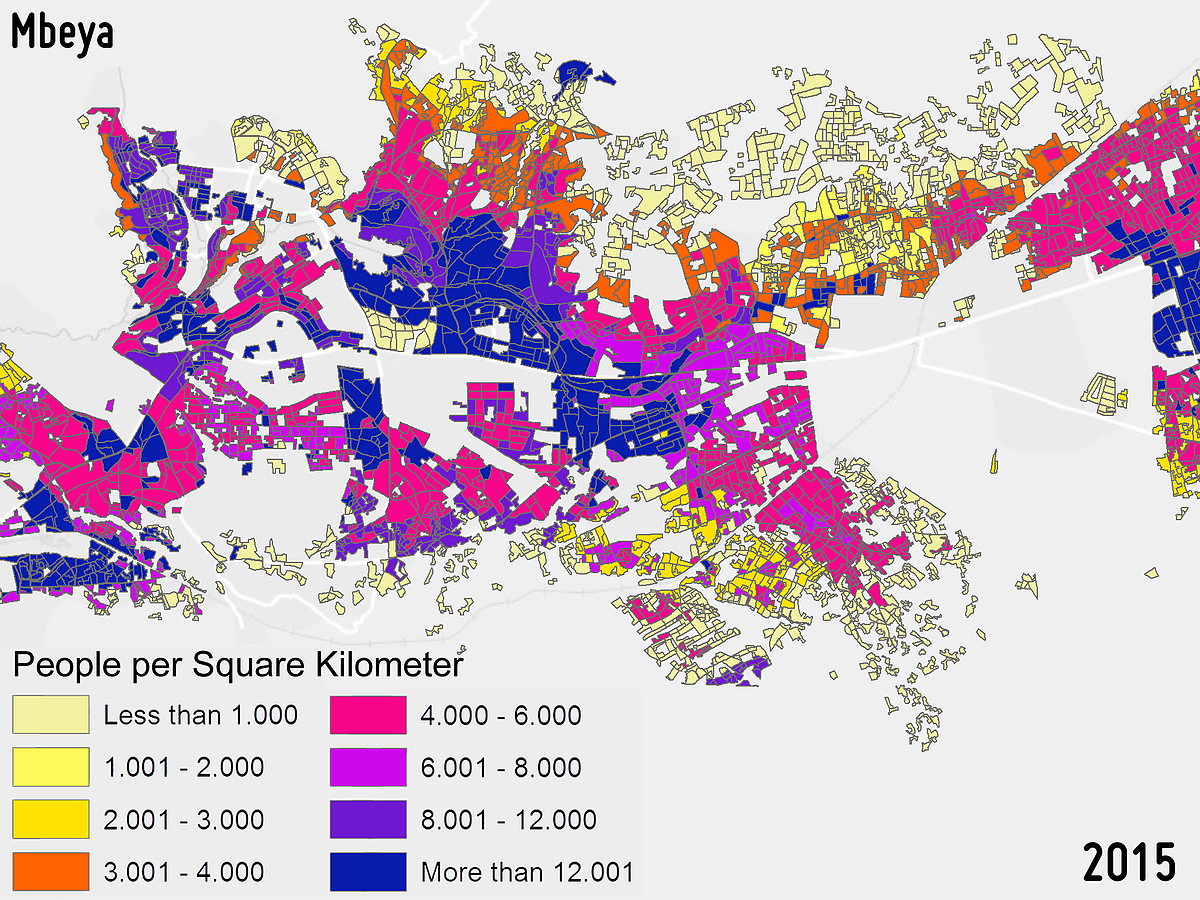
POPULATION DISTRIBUTION AND DENSITY
Population distribution and density assessment are both crucial variables for sustainable urban development and urban security applications (e.g., planning of evacuation measures). The estimation of the urban population distribution and density is an important indicator for the assessment of urban growth and planning for city services. The derived information also supports hazard risk prevention and assessment.
-
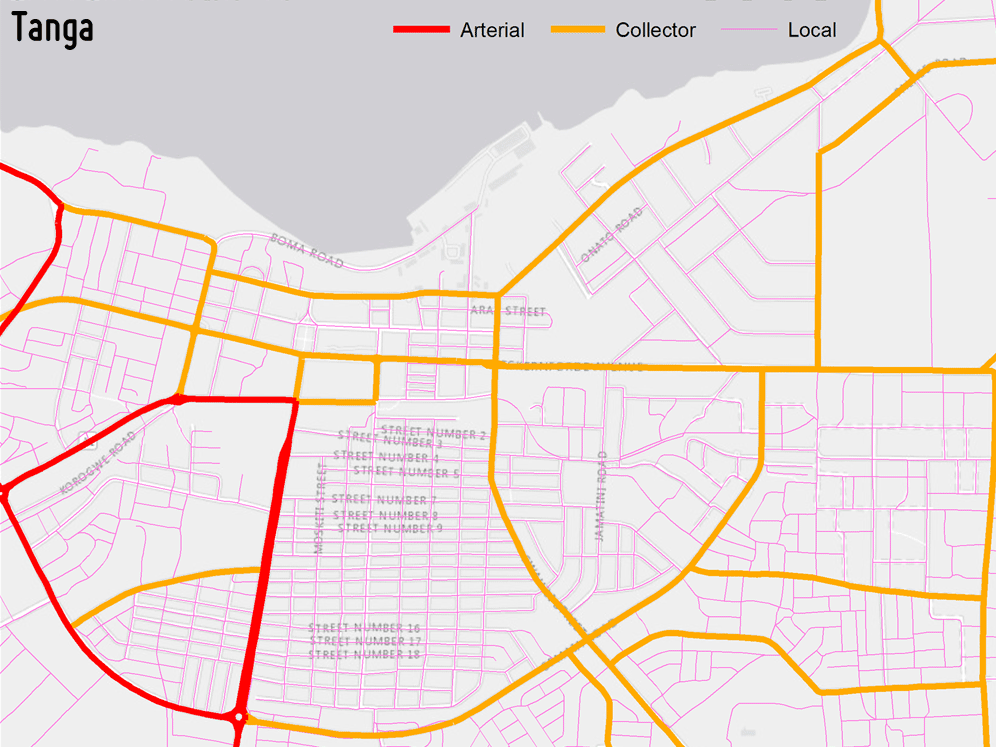
TRANSPORT INFRASTRUCTURE
Maps of the transportation infrastructure can be produced in a harmonized and up-to-date manner by means of very high spatial resolution EO data. This also allows to easily perform frequent updates. The product can be used for manifold spatial analyses as identifying new bus stations, modelling navigation, supporting evacuation plans, as well as finding the shortest path to the nearest hospital or to the closest green area.
(click on “App tour” in the menu bar when accessing)
Where we work
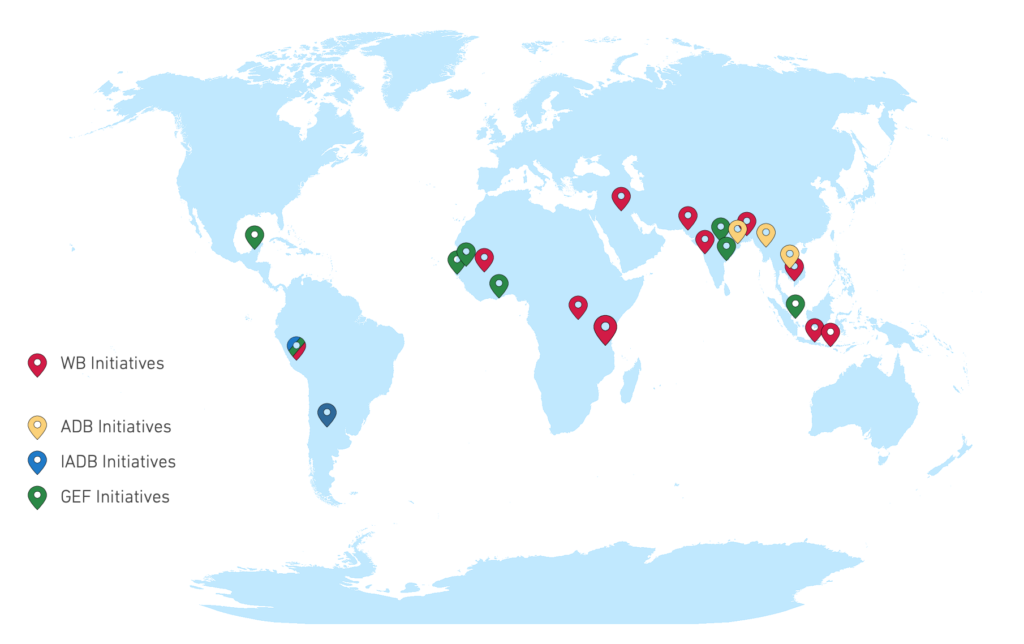
EO4SD-Urban aims at providing support to several initiatives of the World Bank (WB), the Asian Development Bank (ADB), the Inter-American Development Bank (IABD) and the Global Environment Facility (GEF).
In this framework, the list of case studies currently includes 32 cities with an emphasis on low-capacity environments (low- and lower-middle-income developing countries), selected megacities and their hinterlands, and secondary (emerging) cities with a population between approximately 300,000 and 3 million inhabitants. Move the mouse cursor over the place markers in the maps below to discover each of them.
For more details on the supported initiatives, please visit the dedicated page here.
Project Consortium
The Consortium performing the project is composed of eight companies/institutions – lead by GAF AG (Germany) – with deep and complementary EO technical proficiency and wide experience in developing geo-spatial operational services in the urban domain to users in both developing and developed countries. In particular, it includes: SIRS (France), gisat (Czech Republic), egis(France), the German Aerospace Center – DLR (Germany), NEO (The Netherlands), JOANNEUM RESEARCH (Austria), GISBOX (Romania).